Welcome to The Owner’s Guide to Roofing, your comprehensive resource for understanding the essentials of roofing for your property. Whether you’re a homeowner or a commercial property owner, having a basic knowledge of roofing can help you make informed decisions and maintain the integrity of your roof for years to come.
Types of Roofing Materials
Shingle: Popular for residential properties due to their affordability and ease of installation. Shingles come in various styles and colors to match any aesthetic.
Tile: Known for their durability and long lifespan, tiles are a great option for a classic look and excellent weather resistance.
Metal: Ideal for both residential and commercial properties, metal roofs are durable, energy-efficient, and require minimal maintenance.
Flat: Common in commercial buildings, flat roofs offer easy access for maintenance and repairs but require expert installation and waterproofing. TPO is a popular material used on flat roofs.
Wood Shakes: Provide a natural, rustic appearance and are a good choice for specific architectural styles.
Roofing Services
New Roof Installation: When building a new property or replacing an old roof, professional installation ensures longevity and performance.
Re-roofing: An efficient solution for updating and strengthening an existing roof without a full replacement.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance checks and minor repairs can extend the life of your roof and prevent costly damage.
Repairs: Prompt attention to leaks, damaged shingles, or other issues can prevent more significant problems down the line.
Waterproofing
Waterproofing is a crucial aspect of roofing, particularly in areas prone to heavy rainfall or storms like Southwest Florida. Quality waterproofing ensures your roof can withstand the elements, protecting your property from water damage and structural issues.
Choosing the Right Roofing Contractor
Selecting a reputable roofing contractor is vital. Look for a company with experience, positive customer reviews, and a commitment to quality workmanship. A reliable contractor will offer a detailed assessment, clear communication, and a warranty on their services.
By understanding these key aspects of roofing, you can ensure your property remains safe, secure, and visually appealing. Whether you’re considering a new roof, need repairs, or want to explore maintenance options, informed decisions will lead to better outcomes for your property.
Roof Types
There are several common types of roofs, each with its own advantages, aesthetics, and suitability for different climates and building types. Here are some typical types of roofs:
Gable Roof
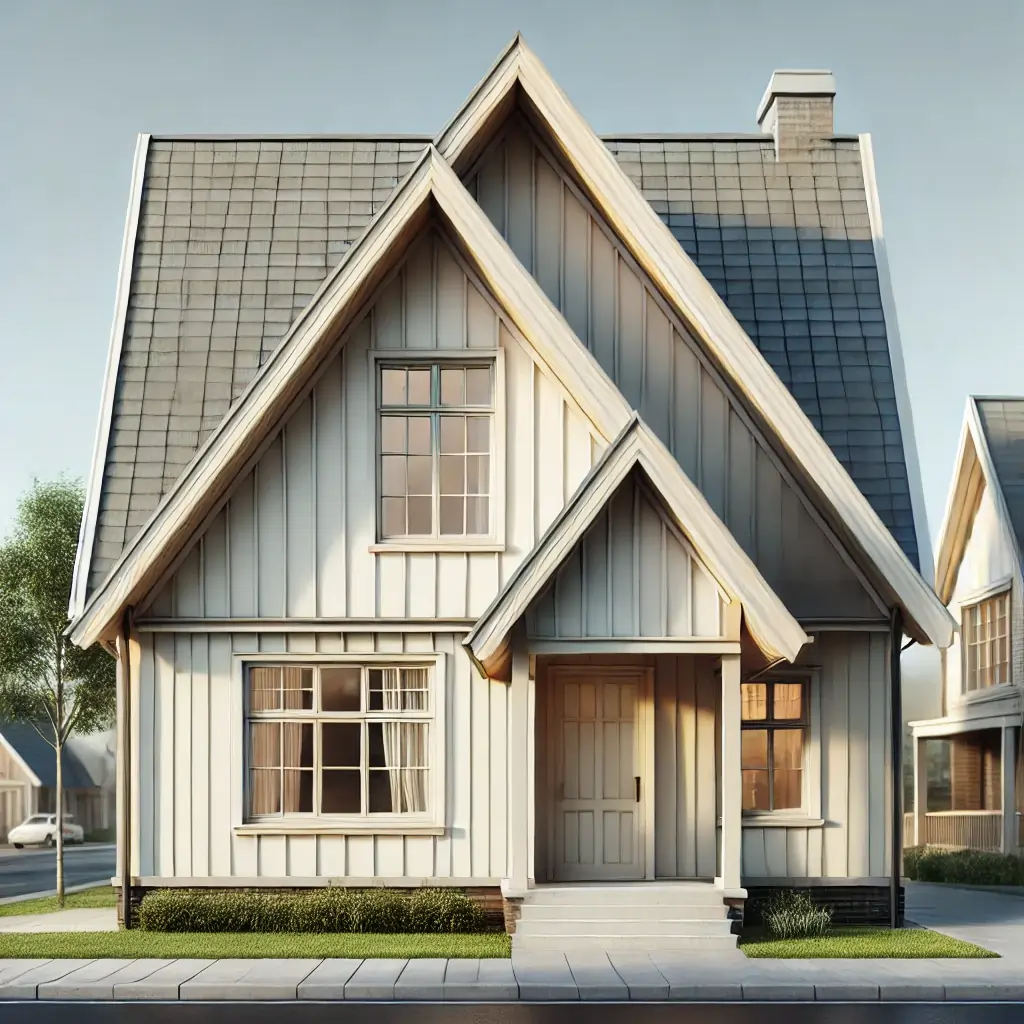

Description: A classic roof type featuring two sloping sides that come together at a ridge, creating end walls with a triangular extension.
Advantages: Simple design, good water drainage, easy to construct.
Hip Roof
Description: All sides slope downwards to the walls, usually with a gentle slope.
Advantages: More stable than gable roofs, better suited for high-wind and snowy areas.
Flat Roof
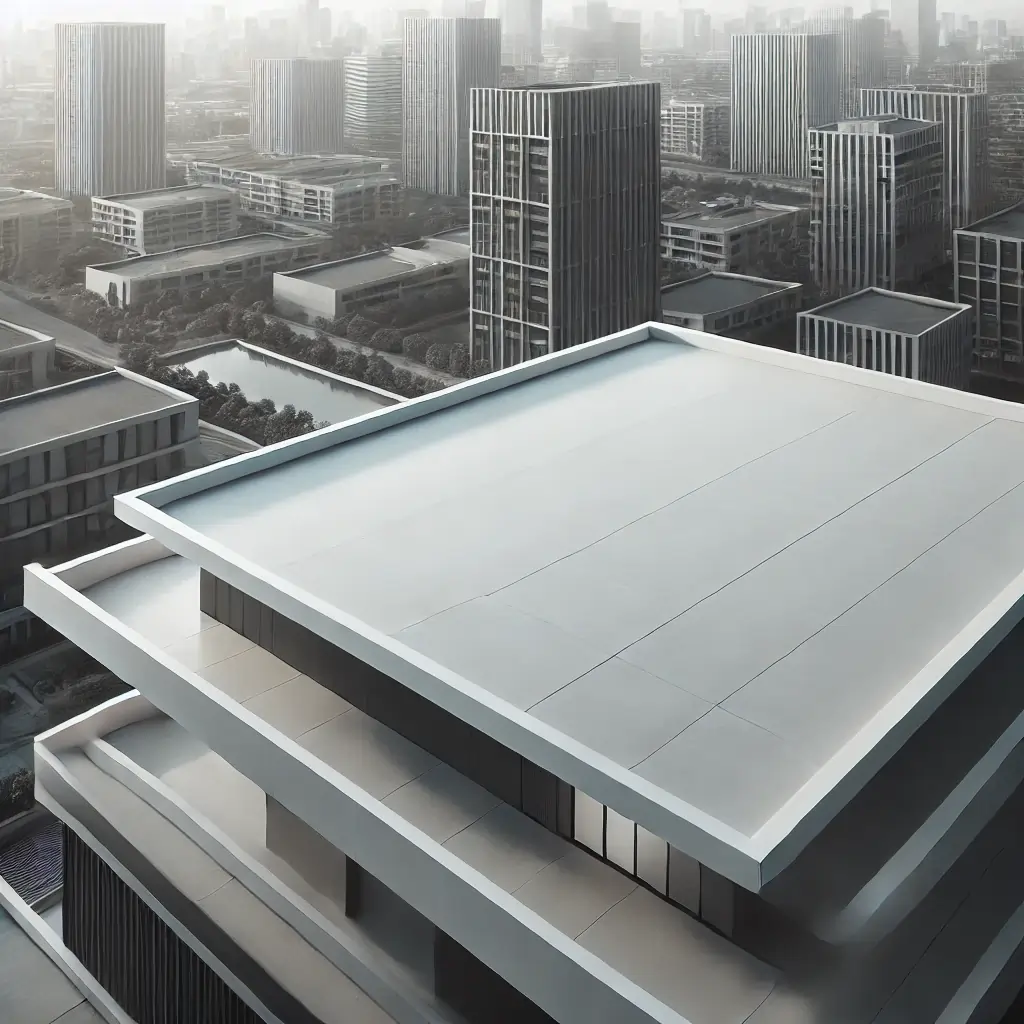

Description: A horizontal or nearly horizontal roof surface.
Advantages: Easier to construct and maintain, can be used as additional living space (e.g., rooftop gardens).
Mansard Roof
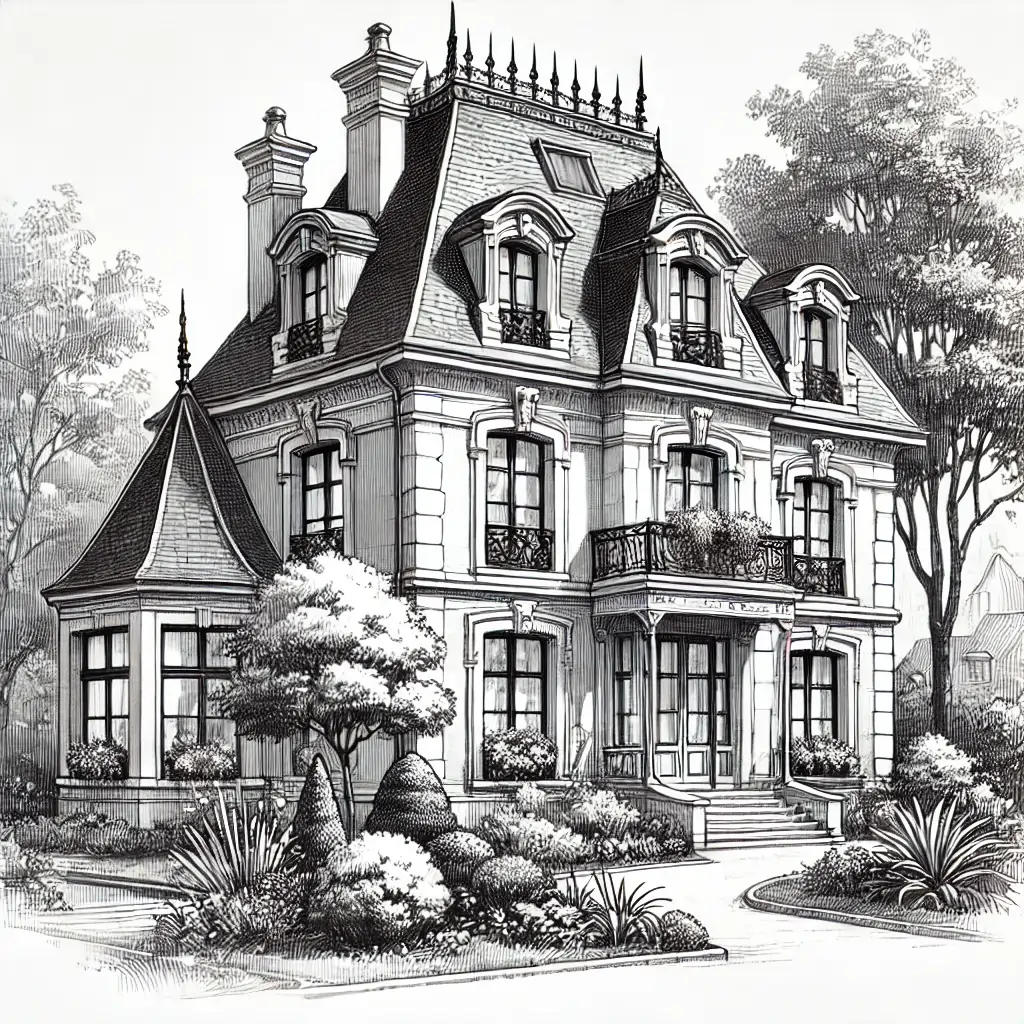

Description: A four-sided gambrel-style hip roof characterized by two slopes on each side, with the lower slope being steeper than the upper.
Advantages: Provides additional living space, aesthetically appealing.
Gambrel Roof
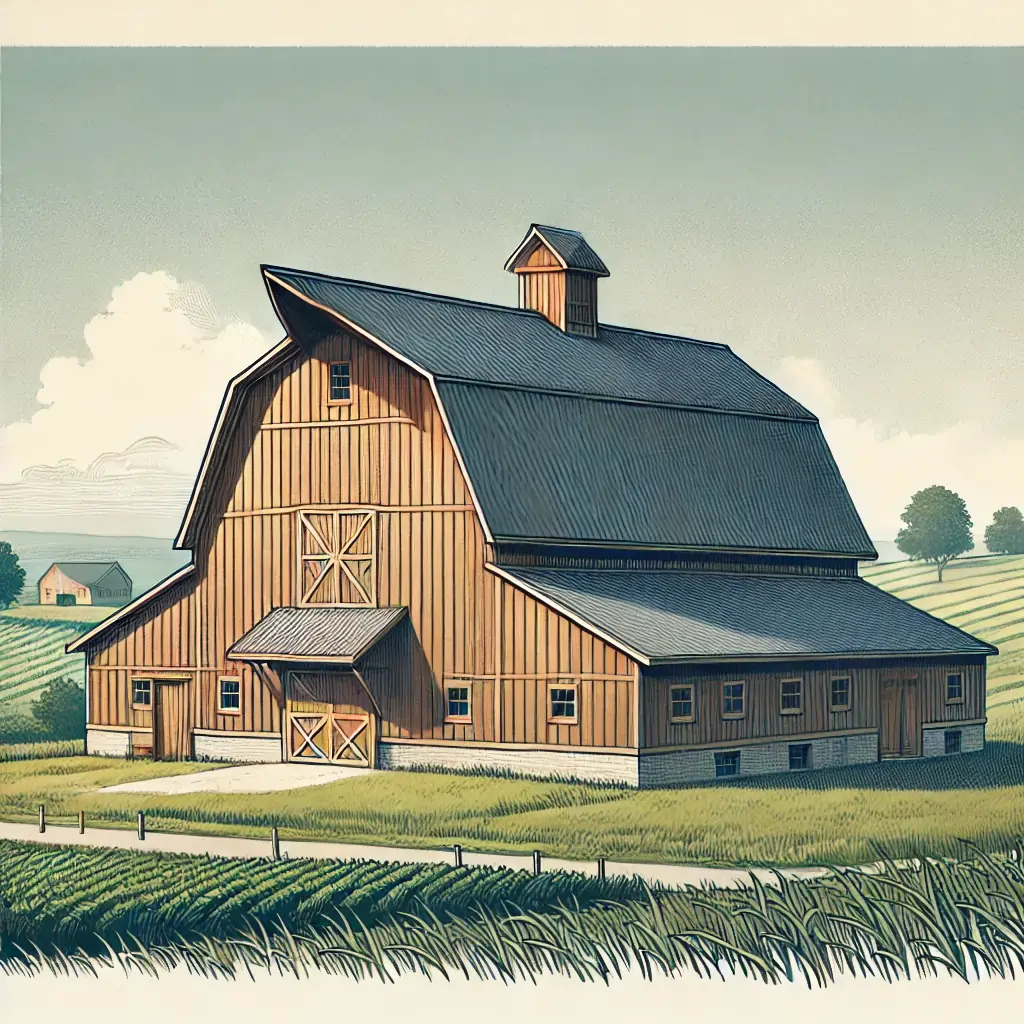

Description: Similar to a mansard but has vertical gable ends and hangs over the facade of the house.
Advantages: Provides extra space, typically used in barns and colonial homes.
Butterfly Roof
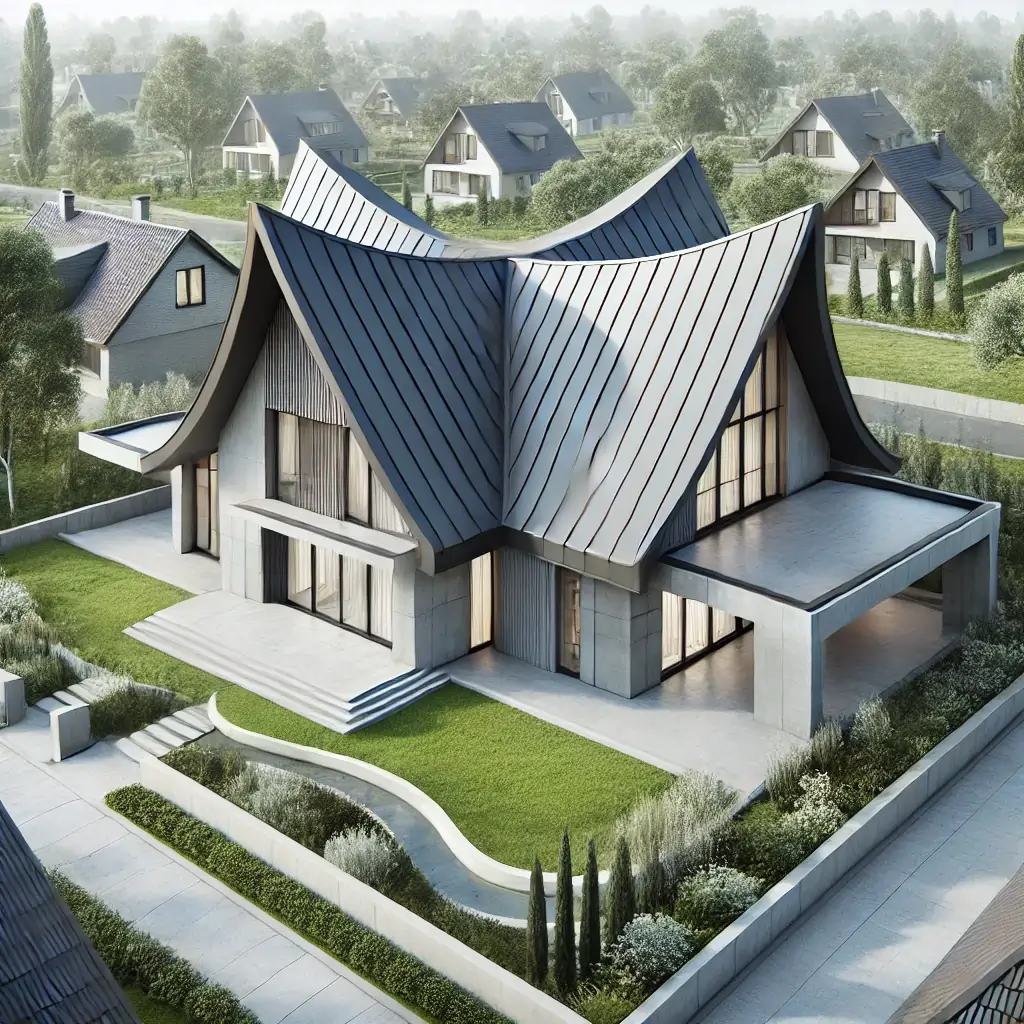

Description: Inverted gable roof with two roof surfaces sloping down from opposite edges to a valley near the middle of the roof.
Advantages: Unique design, allows for larger windows and more natural light.
Bonnet Roof
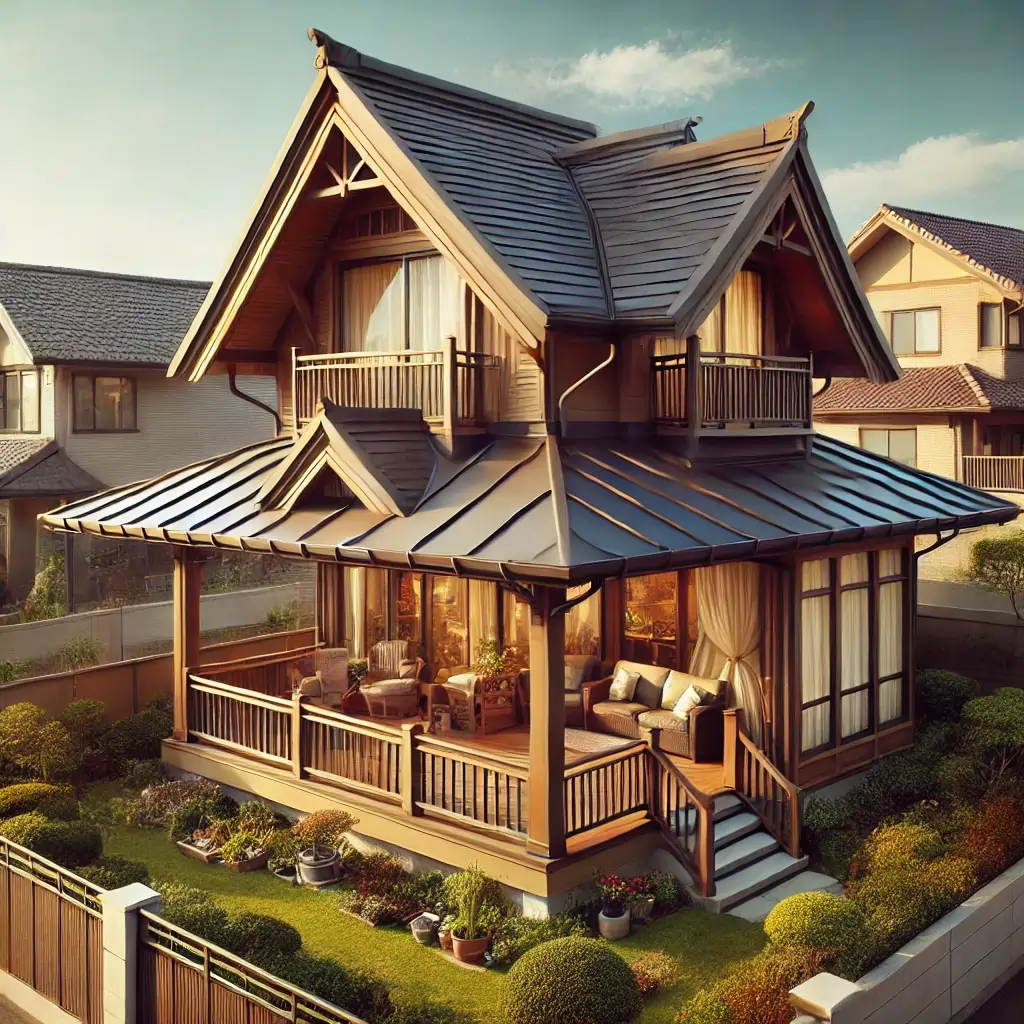

Description: Similar to a hip roof but with lower slopes that extend beyond the house, creating a covered porch area.
Advantages: Provides additional shade, protects the exterior walls from weather.
Skillion Roof
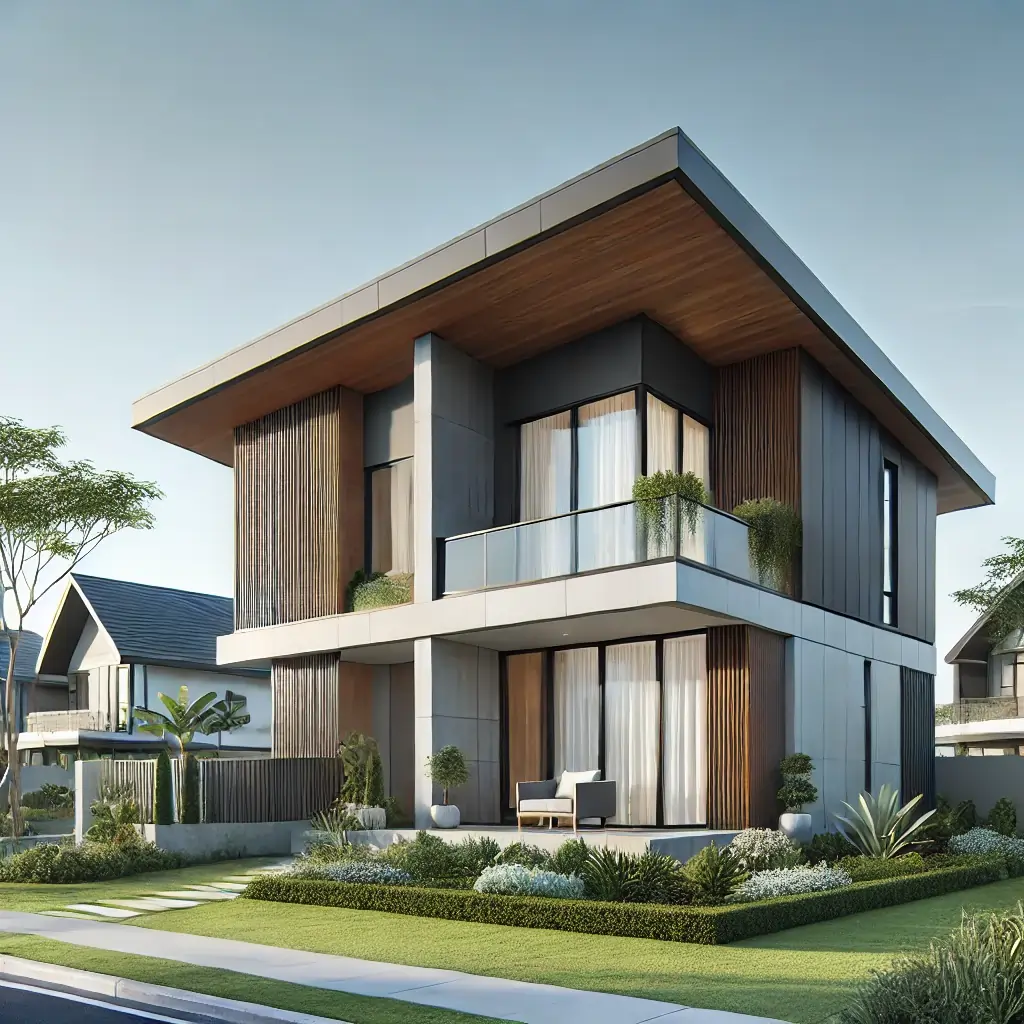

Description: A single sloping roof surface, also known as a shed roof.
Advantages: Simple to construct, ideal for extensions or modern homes.
Saltbox Roof
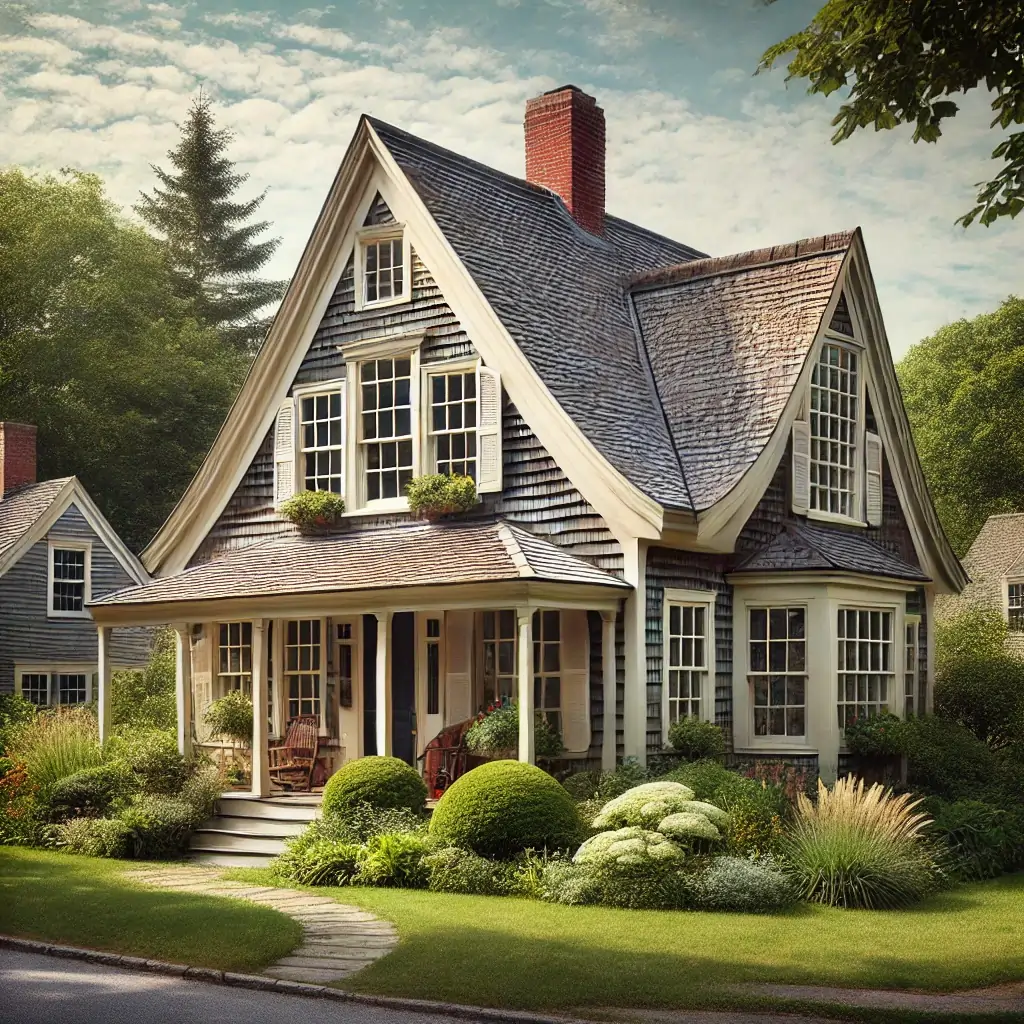

Description: A gable roof with asymmetrical sides, one of which is longer than the other.
Advantages: Adds extra living space, has a distinct, historical look.
Sawtooth Roof
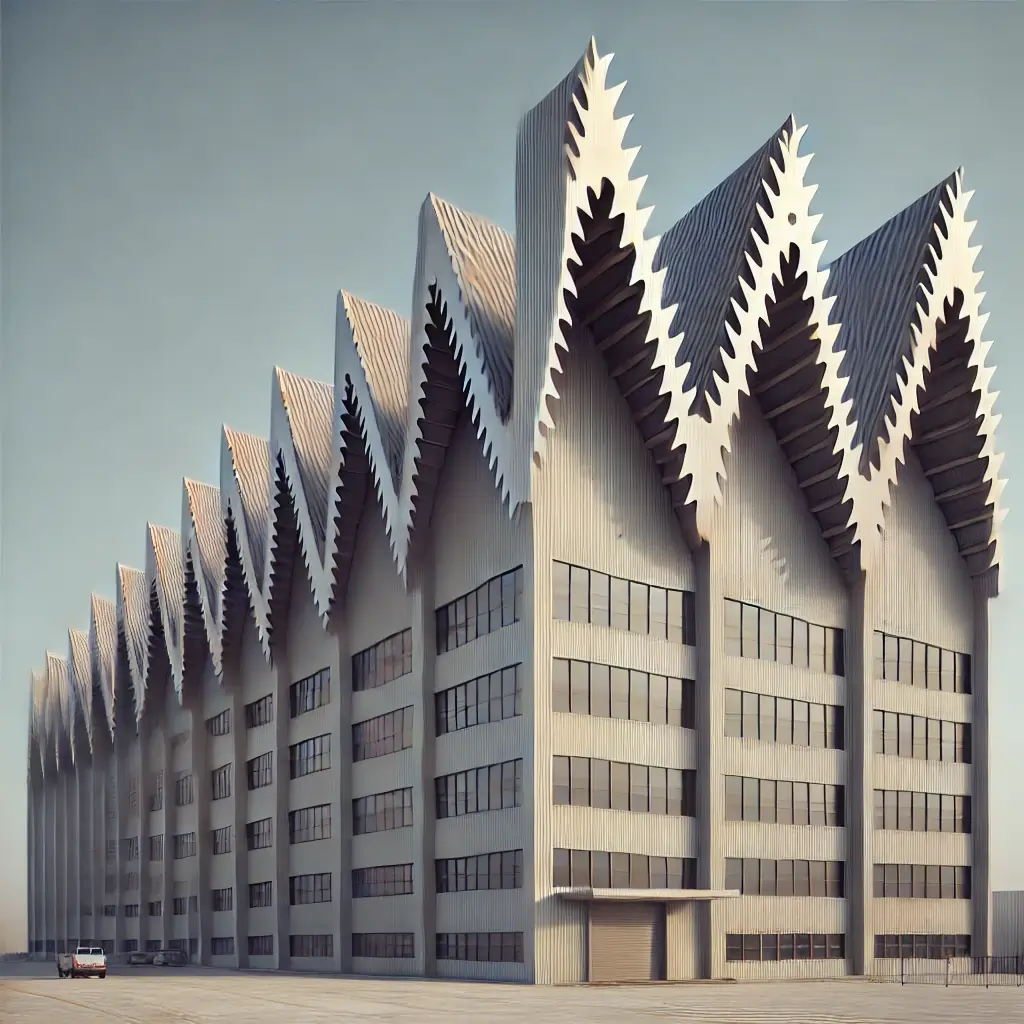

Description: Consists of multiple parallel roofs resembling the teeth of a saw, each with a dual-pitch.
Advantages: Allows for natural light, commonly used in industrial buildings.
Curved Roof
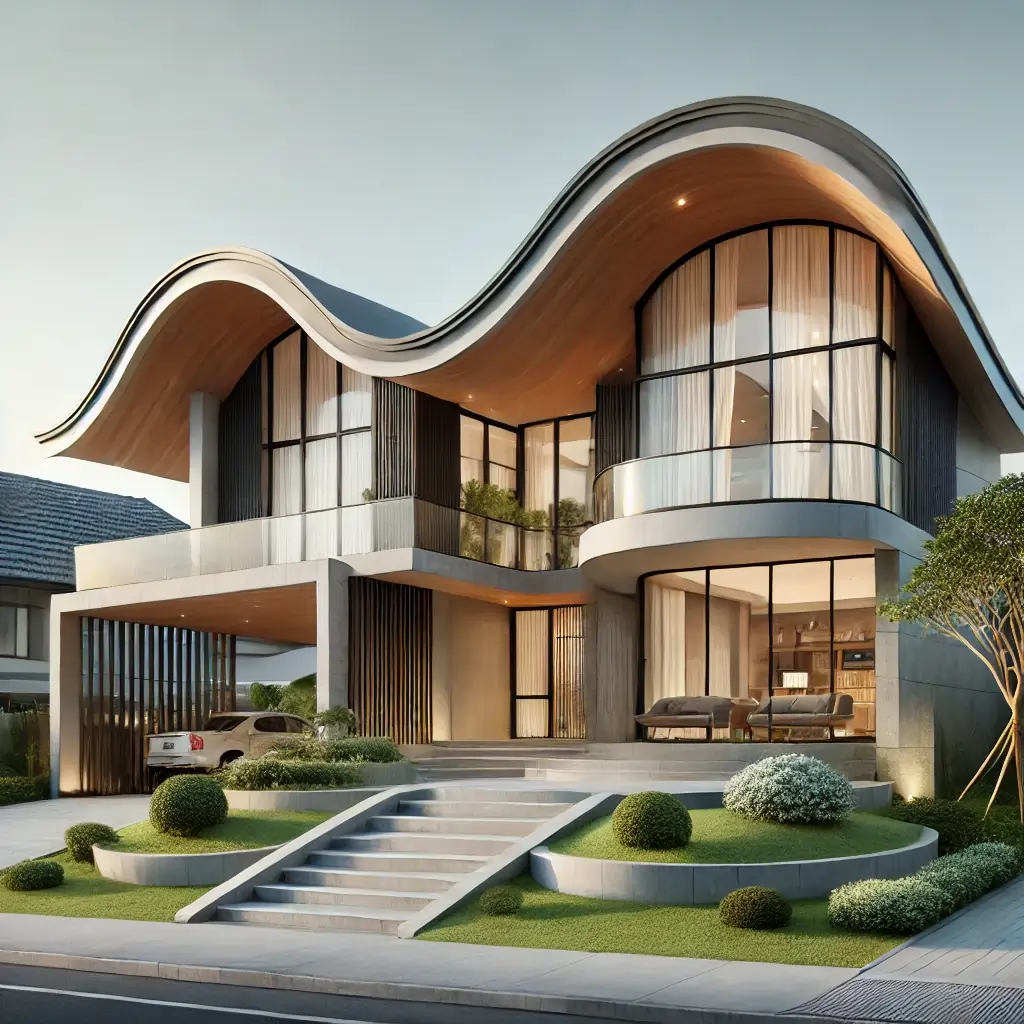

Description: A roof with a curved shape, offering a modern aesthetic.
Advantages: Visually appealing, can be highly energy efficient.
Dormer Roof
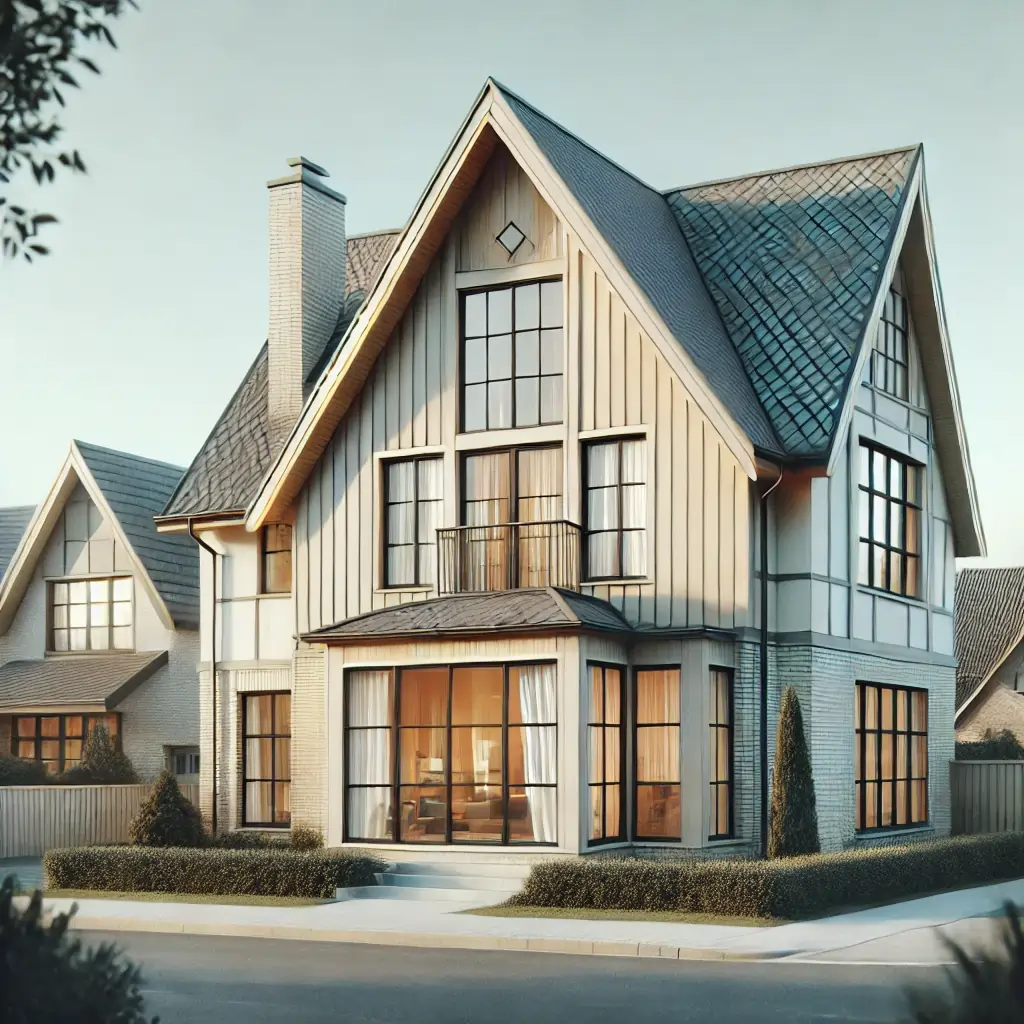

Description: A roofed structure, often containing a window, that projects vertically beyond the plane of a pitched roof.
Advantages: Adds natural light and space to attics or upper stories.
Hips and Valleys Roof
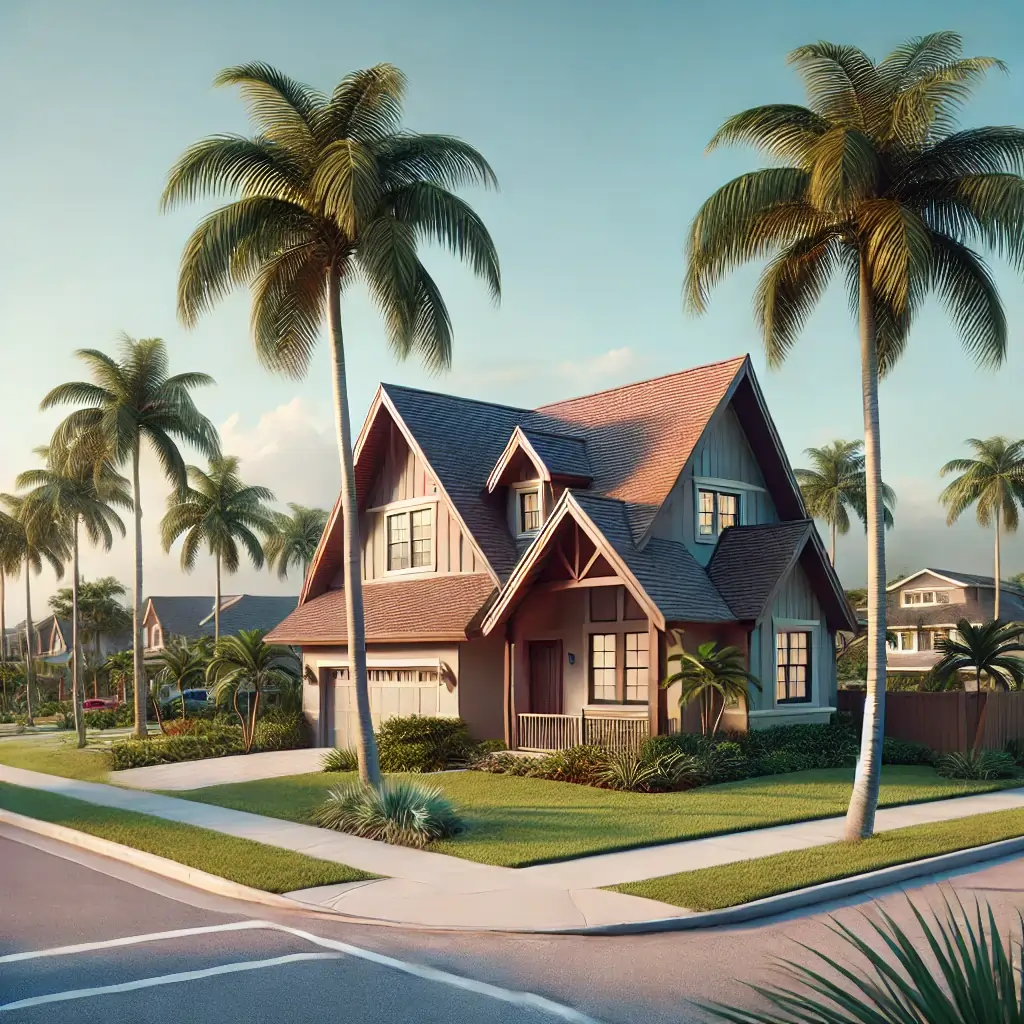

This is by far, the most popular roof type in SWFL.
A hip and valley roof is a complex roofing design that combines the features of both hip roofs and valley roofs. This style involves multiple sloping sides that meet at valleys (the internal angles formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes). The hips are the external angles where two roof slopes meet, while the valleys are the internal angles.
Typically found in more elaborate residential structures, hip and valley roofs offer a distinctive and attractive architectural appearance. This design is particularly effective for homes with irregular or complex layouts, as it can cover various extensions and wings seamlessly.
Advantages of a Hip and Valley Roof
Enhanced Stability:
The interlocking structure of hips and valleys provides superior stability and strength, making it more resistant to high winds and adverse weather conditions.
Improved Water Drainage:
The multiple slopes facilitate efficient water runoff, reducing the risk of water pooling and leaks. This is particularly beneficial in regions with heavy rainfall.
Aesthetic Appeal:
The intricate design of hip and valley roofs adds a visually appealing element to a home, enhancing its overall architectural style and curb appeal.
Versatility:
This roof style is versatile and can be adapted to cover various architectural features, such as dormers, garages, and other extensions, providing a cohesive look.
Increased Home Value:
The aesthetic and functional benefits of hip and valley roofs can contribute to an increase in property value, making them a desirable feature for potential buyers.
Durability:
The design distributes weight more evenly across the structure, which can prolong the lifespan of the roof and the overall building.
Energy Efficiency:
The slopes of the roof can help in deflecting sunlight and reducing heat absorption, potentially lowering cooling costs during hot weather.
Overall, a hip and valley roof combines the best elements of both hip and valley roofs, offering a blend of durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal that can enhance the beauty and performance of a home.
How to Calculate Roofing Areas and Valleys Quickly?
As a property owner, you might need to discuss your total roofing area, or the length of your hips and valleys. How can you know those exact figures without physically getting on your roof and measuring with a measuring tape? Roofing contractors use the flat area and distances (from measuring your floor or looking at your home’s prints) and multiply them by either the roof slope factor or the valley & hip factor. Or, of course, simply call Tarpon Gulf.
Calculating the Area of a Roof
| Roof Slope | Slope Factor* |
|---|---|
| 2 in 12 | 1.0147 |
| 3 in 12 | 1.031 |
| 4 in 12 | 1.054 |
| 5 in 12 | 1.083 |
| 6 in 12 | 1.118 |
| 7 in 12 | 1.158 |
| 8 in 12 | 1.202 |
| 9 in 12 | 1.250 |
| 10 in 12 | 1.302 |
| 11 in 12 | 1.357 |
| 12 in 12 | 1.413 |
Calculating Length of Hips and Valleys
| Roof Slope | Valley and Hip Factor* |
|---|---|
| 2 in 12 | 1.4240 |
| 3 in 12 | 1.4362 |
| 4 in 12 | 1.4530 |
| 5 in 12 | 1.4743 |
| 6 in 12 | 1.5000 |
| 7 in 12 | 1.5298 |
| 8 in 12 | 1.5635 |
| 9 in 12 | 1.6008 |
| 10 in 12 | 1.6415 |
| 11 in 12 | 1.6853 |
| 12 in 12 | 1.7320 |
